Despite some wins, the transition to EHRs has generally been much slower than we anticipated, much harder than we imagined, and it is not hard to argue that interoperability of granular health data remains frustratingly elusive.
"Smart data, smarter healthcare"
Bridging the interop chasms
Case Study: Clinical Engagement
Bridging the gap between the clinical experts and software engineers involved in eHealth projects is well known for being difficult and frustrating for both sides. The openEHR methodology is having great success in bringing the non-technical clinicians along with us on the clinical modelling journey.
Clinical modelling, openEHR style
The outcome of a program of coordinated clinical content standardisation provides a long term and sustainable national approach to developing, maintaining and governing jurisdictional health data specifications. It can form the backbone for a national health data strategy and is a key way to ensure that clinicians contribute their expertise to jurisdictional eHealth programs.
#Uncomplexication of Clinical Infostructure
My presentation delivered remotely from Australia to the Arctic Conference on Dual-Model based Clinical Decision Support & Knowledge Management in Tromsø, Norway today.
The Archetype 'Elevator Pitch'
Technical/Wire...Human/Content
In a comment on one of my most recent posts, Lloyd McKenzie, one of the main authors of the new HL7 FHIR standard made a comment which I think is important in the discourse about whether openEHR archetypes could be utilised within FHIR resources. To ensure it does not remain buried in the rather lengthy comments, I've posted my reply here, with my emphasis added.
Hi Lloyd,This is where we fundamentally differ: You said: "And we don’t care if the data being shared reflects best practice, worst practice or anything in between."
I do. I care a lot.
High quality EHR data content is a key component of interoperability that has NEVER been solved. It is predominantly a human issue, not a technical one - success will only be achieved with heaps of human interaction and collaboration. With the openEHR methodology we are making some inroads into solving it. But even if archetypes are not the final solution, the models that are publicly available are freely available for others to leverage towards 'the ultimate solution'.
Conversely, I don't particularly care what wire format is used to exchange the data. FHIR is the latest of a number of health data exchange mechanisms that have been developed. Hopefully it will be one that is easier to use, more widely implemented and will contribute significantly to improve health data exchange. But ultimately data exchange is a largely technical issue, needs a technical solution and is relatively easy to solve by comparison.
I'm not trying to solve the same problem you are. I have different focus. But I do think that FHIR (and including HL7 more broadly) working together with the openEHR approach to clinical modelling/EHRs could be a pretty powerful combo, if we choose to.
Heather
We need both - quality EHR content AND an excellent technical exchange format. And EHR platforms, CDRs, registries etc. With common clinical archetypes defining the patterns in all of these uses, data can potentially start to flow... and not be blocked and potentially degraded by the current need for transforms, mappings, etc.
The Questionnaire Challenge
How should we model questionnaires in our health data? This is something that @ianmcnicoll and I have grappled with for years. We have reached a conclusion in recent times, and our approach, perhaps rather controversially, is not to model them! Yes, you read me right - as a general principle, don't archetype questionnaires.
Now of course there will be some situations where there are standardised and ubiquitous questionnaires and perhaps it will be reasonable to lock these down as fixed data elements and value sets in an archetype, and maybe even govern them within a CKM environment.
But... Consider the number of questionnaires out 'in the wild' at any point in time. Should each of these be archetyped?
Let's think it through. If there are 5000 questionnaires in the world (and clearly there are way more questionnaires than that out in the health ecosystem) then we would need a corresponding whopping 5000 archetypes. And, as we all know, no two questionnaires will be alike even if they have a common parent document - it is always human nature to 'tweak' each one for local use because 'our situation' is unique. It's just the way it is. The consequences are that any data captured using the myriad of archetypes, even though they may be similar, the data will not be interoperable. We will have a huge number of archetypes with a huge variation in content and intent - not a lot of upside from my point of view.
Another alternative could be to define a generic archetype pattern for a questionnaire, and re-use that. In fact we tried this back in 2007 with our work in the NHS - you can see a reasonable example here. The resulting questionnaire pattern is pretty simple and relies on using the templating layer to document the questions, and either templating or use of a terminology subset to record the answers. The equivalent FHIR resource appears similar in principle and intended use. This kind of pattern provides a common framework for a questionnaire but really doesn't give us a lot more interoperability for questionnaire data - the actual questionnaire content will vary enormously and the results can still be chaotic.
So, still somewhat clunky and awkward - not an elegant solution at all.
Then we got to thinking: Do we always need to actually record the questions and their answers in the EHR? This is a critical question. Sometimes the answer is yes, but most often I think we will find that we don't need to record the actual question and (often) check box response. What we really want to record is the outcome, the real health information meaning.
Think about the practical aspects of this...
Clinicians have a systematic questioning process for history taking - we all have a similar pattern but ask subtly different questions - resulting in zillions of permutations and combinations and levels of granularity. Questions could range from: "Have you had any abdominal symptoms?" to "Have you had any nausea, vomiting, reflux, abdominal pain, diarrhoea, constipation etc" to whatever combination is relevant for a given clinician in a given clinical situation. Many will ask the same kind of question slightly differently. Every resulting questionnaire will be slightly different.
And what do they record? They don't record each question and corresponding Yes/No answers in their paper health records. They record the positive responses or the relevant negatives, and/or maybe a quick note that there were no positive responses to systematic questioning about current symptoms, problems, past history, family history etc.
So we need to ask ourselves: Do we need to record the exact question, the potential alternative answers and the actual answer?
If the answer is yes, then it is a very good reason to lock in the questionnaire in an archetype, or at least a template.
If the answer is no, then what is the best way to record the relevant data - the relevant positives and the relevant negatives. For example, with abdominal pain - record the details about their diarrhoea and colicky pain in the right lower abdomen, PLUS that the patient has NEVER had an Appendicectomy.
So I'm suggesting that we need to record the positive presence of something identified in the questionnaire, for example a symptom, diagnosis or previous procedure, and the positive absence of related things. In this case, record the details about the diarrhoea and abdominal pain as the positive presence of symptoms using the Symptom archetype and positive exclusion of a previous Appendicectomy procedure in the Exclusion of Procedure archetype. We don't need to record the actual question and corresponding Yes/No answer.
So our current approach in Ocean is to use the software UI as the means to display the checklist or questionnaire, but only record in the electronic health record any relevant answers - both the positive presence of symptoms, signs, diagnoses, procedures and tests etc, and also the positive exclusion of any of these things - all using standardised archetypes.
Lets face it, it is not often that we ever go back to look at the raw questionnaire data again. So now we tend not to record the raw data (with some exceptions, where it may be required or useful) but use a transform so that a patient's or clinician's positive tick in a box for 'Past History of Epilepsy?' will be converted into a positive statement of 'Epilepsy' within an EHR, using the Diagnosis archetype. Any additional 'other' free text or 'details' or 'date of diagnosis' from the questionnaire can be captured using other relevant data fields for the Diagnosis archetype. The benefit from this approach is that this data can then be potentially re-used into the future as part of a comprehensive Problem List, not just buried as a ticked check box within a questionnaire from years ago, perhaps never to see the light of day ever again.
Consider the questionnaire as what it really is - just a clinical communication tool, a checklist. It is absolutely not the best means to record, persist and re-use good quality health data. What we really want to record in a consistent way are those critical pieces of health information in a formal archetype so that the data can be utilised for long term health records, decision support, exchange or analysis. Recording the check boxes answers from a questionnaire don't really do that job!
Archetypes in the Real World
I've spent the past week in Ljubljana, Slovenia. Ian McNicoll (@ianmcnicoll) and I were been training clinicians about archetypes and clinical knowledge governance, ready for the launch of their national CKM. A highlight was a side trip to visit the state-of-the-art Paediatric Intensive Care Unit in Ljubljana. The electronic health record has been running there now for two years, with electronic processes gradually taking over. I was escorted by the clinician in charge of the ICU, Professor Kalan. The purpose of the visit – for him to meet someone who facilitated the archetypes used to run his EHR and for me to see our collective international archetype work implemented and used for real clinical purposes, largely under the expert clinical informatics guidance from Ian.

I was thrilled and a little taken aback, all at once. It is one thing to sit in an office researching clinical models and then to remotely collaborate with our international archetype community. But it is another to see real-time data being collected half a world away from home and knowing that we all had a small part in this, especially to support such critical care for a newborn baby. In the photo, above, you might just be able to spot a humidicrib surrounded by all of the equipment.
The majority of these archetypes were built by the international openEHR community for various projects and now utilised under the CC-BY-SA license by the EHR company to develop their clinical system. There are some local archetypes in use as well – added for practical and pragmatic purposes - but these are very much in the minority. These same international archetypes are also being used in the EHR repository in the Northern Territory, Australia, and are underpinning their current work on shared antenatal care and hearing health programs. Soon this work is to be extended for renal failure and heart disease. And across more than 20 sites in Australia we have an infection control system that is using both archetypes and some that have been built specifically to support infection control activities and outbreak management. These shared archetypes are also underpinning work in UK, Brazil, Japan and Sweden.
Next week Ian and I are in Norway to support the Norwegian national archetype effort – training their clinicians and informaticians about archetypes, and especially governance principles at a national level.
There are now 5 CKMs in existence:
- the openEHR international CKM;
- Australia;
- City of Moscow;
- UK clinical community; and the brand new
- Slovenian eHealth program CKM.
The international CKM will continue to gather quality archetypes from all sources and coordinate international review and modelling activities. The intent is for this CKM to be the first port of call for those looking for an archetype.
The national-, organisation- or program-based CKMs will be focussed on supporting local health IT activities and will leverage the international pool of archetypes by a virtual 'read only' reference capability as well as hold specific local archetypes or modifications of the international archetypes that will support local implementation.
Above all the aim is to create high quality, computable, clinical content definitions that have been developed and ratified by the clinicians themselves. In turn this will support collection of good quality data that can be used for a variety of purposes – ranging from the health record itself; through querying and knowledge-based activities such as decision support; aggregation, analysis and research; and secondary use, including population health activities.
I have said it before, but let me say it again…
IT. IS. ALL. ABOUT. THE. DATA.
In the discussions about standards, the standardisation of data is usually missed.
Seeing this little baby in a humidicrib in amongst all of the 'machines that go beep' has invigorated me again.
Let's continue, and even accelerate, our collaboration on the development of archetypes. This will enable us to gather the data we need to provide the kind of healthcare our patients deserve.
We need the domain experts!
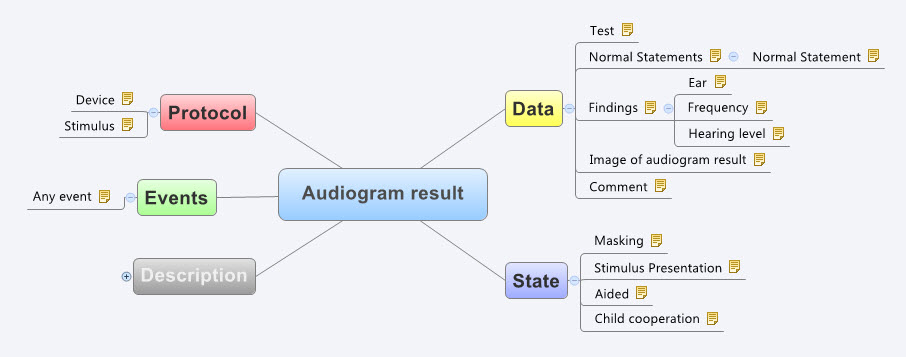
It certainly helps to be a clinician, although recent work on development of clinical content specifications for a Hearing Health application has taken me further into modelling for the range of audiometry, 226Hz and high frequency tympanometry, audiology speech testing, and hearing screening than I’d ever imagined. Modelling the raw data capture (or downloaded from devices) for these tests is really quite simple, but enabling the complexity of different states, events and protocols that reflect audiological practice has been much more complex than I anticipated. I attempted to model these some years ago, based on my (obviously rather poor) research on the web at the time. Take a look at my meagre effort to build the original archetype for Audiogram Result (as built by a GP who has never performed an audiogram).
See the full detail here - http://www.openehr.org/ckm/#showArchetype_1013.1.44_1
And the most recent archetype as designed and verified by practising grassroots Audiologists… I didn’t even get the name of the concept correct!
See the full detail here - http://dcm.nehta.org.au/ckm/#showArchetype_1013.1.1097
Identifying domain experts for the development and then collaboration on verification/validation of each type of archetype/template is absolutely critical for success.
Engaging clinicians: building EHR specifications
There is a methodology that is pragmatically evolving from my experience in openEHR clinical modelling work over the past few years. It has developed in a rather ad hoc way, and totally in response to working directly with clinicians. The simplicity and apparent effectiveness – both for me and the clinicians involved - continues to surprise me each time I use it. The clinical content specifications for specialised health records and care plans that we are building are being developed with a sequence of expert input and clinical verification:
- Identifying the clinical requirements and business rules in conjunction with a selected initial domain expert group;
- Broader abstract verification of the notion of ‘maximal data set’ for ‘universal use case’ during formal archetype review cycles;
- Contextual validation during template review by ‘on-the-ground’ clinicians; and finally, although to a lesser degree,
- Validation during mapping and migration of legacy data.
With each project I am refining this process. Starting off a project with face-to-face meetings has been a ‘no brainer’ – after all, it takes a while for everyone to understand the get the idea of what we are doing. However after initial workshops, pretty much everything else can be done via web conference, online collaboration via CKM and email.
I find the initial workshops are usually greatly satisfying. Within hours we can be creating two outputs – a mind map that reflects the clinicians evolving conversation about their requirements and, in parallel, an equally agile template of clinical content specifications that can be verified by the clinicians in real time.
The mind map is displayed on a shared screen or via a data projector and acts as a living document, evolving as we talk through the clinical requirements, and identify the complexities, dependencies and relationships of all the components. The final mind map may be surprisingly different to how it started, and at the end of the conversation, the clinicians can verify that what they’ve said if accurately reflected in the mind map. It is an open source tool, so we can also share this around after the workshop for further comments.
Most recently I have begun building a template on the fly during the workshop, using any existing archetypes that are available, and identifying gaps or the need for new archetypes on the mind map as we go. In this way we are actually building the content specification in front of the clinicians as well. They get an understanding of how the abstract discussion will actually shape the resulting EHR content and they can verify it as we gradually pull it together. The domain experts are immediately equipped to answer the question: “Does this specification match what you have been telling me you do in practice?”
This methodology seems to bring the clinicians along with us on the clinical modelling journey, and most are able to understand at least some of the implications of some of our requirements discussions and, in particular, the ‘shape’ of the data that we can collect. It is a process seems to suit the thinking process of many clinicians and the overwhelmingly consistent feedback from recent workshops is that they have all actually enjoyed the experience and want to know what are the next steps for them to be involved. So that’s certainly a winner.
And the funders/jurisdictions are anecdotally confirming for me that they are finding that this approach is supporting higher quality specifications in a much shorter time frame.
For example, at a project kickoff workshop for a new project recently, in two days we:
- developed a series of mind maps capturing a consensus view of the clinical requirements and business processes;
- identified all the archetypes required for the entire project, including those that existed and were ‘fit for use’, those that needed some extension to meet requirements and new archetypes that needed to be created;
- identified sources of information or mind mapped the requirements for each new archetype identified; and
- built 3 templates comprising all of the existing archetypes available from a number of sources – the NEHTA CKM http://dcm.nehta.org.au/ckm/, the openEHR international CKM http://www.openehr.org/ckm/ and local drafts that I had on my own computer. For a number of the new archetypes we also collectively identified source information that would inform or be the basis for the archetype development.
All of this described above took 8 medical practitioners clinicians away from their everyday practice for only 1-2 days, each according to their availability. Yet it provided the foundation for development of a new clinical application.
Then I go home. Next steps are to refine the mind map, modify/update/specialise any archetypes for which we have identified new requirements and build the new ones. And in parallel start the collaborative process through a CKM project to ensure that existing and modified archetypes are ‘fit for (our project’s) purpose’, and to upload and initiate reviews on the new draft archetypes.
All work to progress these archetypes to maturity (ie aiming for clinical consensus) and then validate the templates as ready for handover to the implementers can be done online, asynchronously and at a time convenient to the clinicians work/life balance!
I live over 2000 kilometres away from these clinicians. Yet the combination of web conference and CKM enables us to operate as an ongoing collaborative team. It seems to be working well at the moment... No doubt I'll continue to learn how to do it better.
The Archetype Journey...
I'm surprised to realise I've been building archetypes for over 7 years. It honestly doesn't feel that long. It still feels like we are in the relatively early days of understanding how to model clinical archetypes, to validate them and to govern them. I am learning more with each archetype I build. They are definitely getting better and the process more refined. But we aren't there yet. We have a ways to go! Let me try to share some idea of the challenges and complexities I see…
We can build all kinds of archetypes for different purposes.
There are the ones we just want to use for our own project or purpose, to be used in splendid isolation. Yes, anyone can build an archetype for any reason. Easy as. No design constraints, no collaboration, just whatever you want to model and as large or complex as you like.
But if you want to build them so that they will be re-used and shared, then a whole different approach is required. Each archetype needs to fit with the others around it, to complement but not duplicate or overlap; to be of the same granularity; to be consistent with the way similar concepts are modelled; to have the same principles regarding the level of detail modelled; the same approach to defining scope; and of course the same approach to defining a clinical concept versus a data element or group of data elements… The list goes on.
Some archetypes are straightforward to design and build, for example all the very prescriptive and well recognised scales like the Braden Scale or Glasgow Coma Scale. These are the 'no brainers' of clinical modelling.
Some are harder and more abstract, such as those underpinning a clinical decision support system of orders and activities to ensure that care plans are carried out, clinical outcomes achieved and patients don't 'fall through the cracks' from transitions of care.
Then there are the repositories of archetypes that are intended to work as single, cohesive pool of models – each archetype for a single clinical concept that all sits closely aligned to the next one, but minimising any duplication or overlap.
That is a massive coordination task, and one that I underestimated hugely when we embarked on the development of the openEHR Clinical Knowledge Manager, and especially more recently, the really active development and coordination required to manage the model development, collaboration and management process within the Australian CKM – where the national eHealth program and jurisdictions are working within the same domain of models, developing new ones for specific purposes and re-using common, shared models for different use cases and clinical contexts.
The archetype ecosystems are hard, numbers of archetypes that need to work together intimately and precisely to enable the accurate and safe modelling of clinical data. Physical examination is the perfect example that has been weighing on my mind now for some time. I've dabbled with small parts of this over the years, as specific projects needed to model a small part of the physical exam here and there. My initial focus was on modelling generic patterns for inspection, palpation, auscultation and percussion – four well identified pillars of the art of clinical examination. If you take a look at the Inspection archetype clinicians will recognise the kind of pattern that we were taught in First Year of our Medical or Nursing degrees. And I built huge mind maps to try to anticipate how the basic generic pattern could be specialised or adapted for use in all aspects of recording the inspection component of clinical examination. Over time, I have convinced myself that this would not work, and so the ongoing dilemma was how to approach it to create a standardised, yet extraordinarily flexible solution.
Over time, I have convinced myself that this would not work, and so the ongoing dilemma was how to approach it to create a standardised, yet extraordinarily flexible solution.
Consider the dilemma of modelling physical examination. How can we capture the fractal nature of physical examination? How can we represent the art of every clinician's practice in standardised archetypes? We need models that can be standardised, yet we also need to be able to respond to the massive variability in the requirements and approach of each and every clinician. Each profession will record the same concept in different levels of detail, and often in a slightly different context. Each specialty will record different combinations of details. Specialists need all the detail; generalists only want to record the bare basics, unless they find something significant in which case they want to drill down to the nth degree. And don't forget the ability to just quickly note 'NAD' as you fly past to the next part of the examination; for rheumatologists to record a homunculus; for the requirement for addition of photos or annotated diagrams! Ha – modelling physical examination IS NOT SIMPLE!
I think I might have finally broken the back of the physical examination modelling dilemma just this week. Seven years after starting this journey, with all this modelling experience behind me! The one sure thing I have learned – a realisation of how much we don't know. Don't let anyone tell you it is easy or we know enough. IMO we aren't ready to publish standards or even specifications about this work, yet. But we are making good, sound, robust progress. We can start to document our experience and sound principles.
This new domain of clinical knowledge management is complex; nobody should be saying we have it sorted...
The White Wizard is Walking
I received my Walking Jacket at the reception desk of my Italian hotel. I'd just paid an exorbitant amount of tax in exchange for receive my jacket from the Italian Postal Service for my trusty, favourite jacket to be turned into a disruptive artwork by @ReginaHolliday. I first wore it to the Medical Informatics Europe Conference in Pisa in August 2012 and then to the ISO TC 215 meeting in Vienna the following September. I'd heard about Regina and her family's story some time before, my awareness raised purely through the twitter community, and then finding images of her 73 cents mural. I finally met her at HIC12, the Australian health informatics conference in Sydney in early August.
Regina was a keynote speaker and during her HIC address, many in the audience were clearly moved. It is the only presentation that I have seen in the health IT environment that received a standing ovation – powerful stuff. It polarised people. Most loved it and felt inspired; some thought it inappropriate in a healthIT conference – go figure!
Regina and I talked one night at dinner. She offered to paint me a jacket. I felt a bit like a fraud – I have no special patient data faux pas story to tell. My involvement in health IT stems from having a long-term engagement with the health system from the tender age of 5; about how that influencing my decision to become a doctor; and my subsequent, almost accidental, slip sideways into health informatics. Nowadays my work focus is firmly on getting health data right, working collaboratively with international clinicians to agree on common definitions about how to represent clinical content in electronic health records.
 And yet here is my jacket – a favourite that I bought way back in 2000 for my first foray out of clinical practice and into the corporate world - my first step into health informatics. I hadn't worn it for a while and Regina's painting has given it a new lease of life. It now has its own story - having travelled to the US to be painted, on to Europe to be worn for the first time in Italy and Vienna, and now back home to Australia.
And yet here is my jacket – a favourite that I bought way back in 2000 for my first foray out of clinical practice and into the corporate world - my first step into health informatics. I hadn't worn it for a while and Regina's painting has given it a new lease of life. It now has its own story - having travelled to the US to be painted, on to Europe to be worn for the first time in Italy and Vienna, and now back home to Australia.
Regina hasn't explained the image to me. I've asked … and waited. She promised to blog about it, but I think I'll be waiting a while. In her gallery of jackets that tell personal stories, mine is number 176.
So let me share what I think it portrays…
I was hit by a car when I was five years old. As a result I started my first day of school on crutches and in plaster from my waist to my right ankle – that young girl on crutches and wearing a caliper is me. Mini-me!
That accident resulted in some permanent problems and I ended up experiencing a series of operations during my childhood and early teenage years. Way too much time was spent in hospital than was healthy, but I still remember telling my orthopaedic surgeon that I wanted to be a Nurse. I remember him saying 'Rubbish. You shouldn't do that much walking. You should be a Doctor, instead"! Maybe it planted a seed. I don't remember it influencing my decision to enter medicine, but that is where I found myself. I'm not sure that as a young intern and resident years we walked less than the nurses – my memory is we never stopped running!
I practiced medicine for over 15 years, gradually side-stepping into health informatics as I joined my husband in developing, marketing, selling, supporting one of the first prescribing systems in Australia. He was the geek GP, passionate to combine his love of clinical practice with technology. I merely agreed to support him in his venture, having absolutely no idea what I was getting myself into.
That kickstarted the health informatics chapter of my life – 17 years duration to date - which has propelled my husband and myself jointly into the world of business, from cottage industry to large corporate consulting firms, and travel to some extraordinary places.
 The adult woman in Regina's image is also me – as the 'omowizard'. This has become my online persona, largely now related to Twitter and blogging. 'omowizard' originated from a love of Tolkien and seeking a Hotmail account back in 2000. Gandalf was taken, as was the 'white wizard'. So given my laundry responsibilities for my young family at the time, I became whiter than white – the Omo wizard. For those unaware, Omo is a brand of clothes washing powder that at the time claimed to wash clothes 'whiter than white'! I never dreamed anyone else would ever have to know or understand that, not even when I experimented on Twitter for the first time as @omowizard. Now it is probably too late to change :)
The adult woman in Regina's image is also me – as the 'omowizard'. This has become my online persona, largely now related to Twitter and blogging. 'omowizard' originated from a love of Tolkien and seeking a Hotmail account back in 2000. Gandalf was taken, as was the 'white wizard'. So given my laundry responsibilities for my young family at the time, I became whiter than white – the Omo wizard. For those unaware, Omo is a brand of clothes washing powder that at the time claimed to wash clothes 'whiter than white'! I never dreamed anyone else would ever have to know or understand that, not even when I experimented on Twitter for the first time as @omowizard. Now it is probably too late to change :)
In the painting I am standing in isolation on a very tall, narrow, bleak pillar. I'm not quite sure what that is representing. Some have suggested a reference to Sauron's tower in Lord of the Rings, but maybe that's too fanciful! I certainly don't have any magic powers. My youngest child informed me recently that I have a strong maternal death stare as a superpower, but I don't think that counts. Maybe it represents the approach that we have been using to standardise the clinical content for health records. It is known as openEHR and although I have been heavily involved in developing the clinical modelling side of it – building archetypes and training others. It has stood in isolation for many years and outside of the mainstream approaches to health IT, but in recent years has become recognised and is gaining increasing recognition as a significant contributor towards the goal of semantic interoperability. Only Regina knows the answer to this one!
 The ribbons or strands entwining around the tower are really interesting to me. The main one rippling across the tower reads: "A house divided against itself cannot stand". This appears to be a direct reference to Jesus' words in Matthew 12:25 – "He knew what they were thinking and told them, "Every kingdom divided against itself is destroyed, and every city or household divided against itself will not stand." (NIV 2012). Abraham Lincoln used the phrase in a speech to Republican candidates at the Republican State Convention on June 16, 1858 relating to the danger of slavery-based disunion. Apparently it is still used sometimes in political speeches, calling for unity and working together for a common goal.
The ribbons or strands entwining around the tower are really interesting to me. The main one rippling across the tower reads: "A house divided against itself cannot stand". This appears to be a direct reference to Jesus' words in Matthew 12:25 – "He knew what they were thinking and told them, "Every kingdom divided against itself is destroyed, and every city or household divided against itself will not stand." (NIV 2012). Abraham Lincoln used the phrase in a speech to Republican candidates at the Republican State Convention on June 16, 1858 relating to the danger of slavery-based disunion. Apparently it is still used sometimes in political speeches, calling for unity and working together for a common goal.
The lowest ribbon says simply, 'openEHR'; the one immediately to its right, 'HL7'; and just above it, 'Standards and Interoperability'.
I had described the approach that we are taking with our openEHR clinical modelling to Regina as one in which we are engaging with clinicians and domain experts to verify that the computable definitions that we are building in openEHR systems are fit for purpose. It is a collaborative approach that is crowdsourcing clinical expertise using the Clinical Knowledge Manager tool. For many years there had been little engagement with the HL7 community as a whole, although recently there appear to have been a softening of the lines of political demarcation. Those not constrained by political blinkers can see there could be significant mutual benefit from openEHR content definitions being used within HL7 constructs. Who knows if this will eventuate? And then there are other opportunities such as the CIMI and FHIR projects… Collaborating is the key.
So I interpret the ribbons yielded by the omowizard as another way of Regina calling for collaboration and collective action in healthIT. It seems that she is portraying me as a coordinator of some of the standardisation occurring in healthIT around the archetype work – using the @omowizard's twitter and blogging being one of the means to coordinate and share the passion, perhaps!
I love the painting but in trying to interpret it, it is not a comfortable image for me. I don't like being the focus. I am certainly enjoying my small bit part in the openEHR clinical modelling and health IT standards world. I have come to openEHR when it was relatively immature. We are seeing it grow and become established, but it is definitely not my idea or vision. I'm just one of number who have had the exciting opportunity of being a facilitator for something that I believe will make a difference.
I hope that when I wear this jacket it will trigger some discussions that might further progress in sharing health information and impacting the provision of health care – that is reason enough to wear it.
Thankyou, Regina. My jacket is a piece of art that is beautiful to look at; It is a powerful statement when understood in context of its origins; and is potentially a disruptive force when considered as part of the larger international Walking Gallery movement. I look forward to more opportunities to wear it at home in Australia and in my travels.
Archetype Re-use
Last Thursday & Friday @hughleslie and I presented a two day training course on openEHR clinical modelling. Introductory training typically starts with a day to provide an overview – the "what, why, how" about openEHR, a demo of the clinical modelling methodology and tooling, followed by setting the context about where and how it is being used around the world. Day Two is usually aimed at putting away the theoretical powerpoints and getting everyone involved - hands on modelling. At the end of Day One I asked the trainees to select something they will need to model in coming months and set it as our challenge for the next day. We talked about the possibility health or discharge summaries – that's pretty easy as we largely have the quite mature content for these and other continuity of care documents. What they actually sent through was an Antineoplastic Drug Administration Checklist, a Chemotherapy Ambulatory Care Nursing Intervention and Antineoplastic Drug Patient Assessment Tool! Sounded rather daunting! Although all very relevant to this group and the content they will have to create for the new oncology EHR they are building.
Perusing the Drug Checklist ifrst - it was easily apparent it going to need template comprising mostly ACTION archetypes but it meant starting with some fairly advanced modelling which wasn't the intent as an initial learning exercise.. The Patient Assessment Tool, primarily a checklist, had its own tricky issues about what to persist sensibly in an EHR. So we decided to leave these two for Day Three or Four or..!
So our practical modelling task was to represent the Chemotherapy Ambulatory Care  Nursing Intervention form. The form had been sourced from another hospital as an example of an existing form and the initial part of the analysis involved working out the intent of the form .
Nursing Intervention form. The form had been sourced from another hospital as an example of an existing form and the initial part of the analysis involved working out the intent of the form .
What I've found over years is that we as human beings are very forgiving when it comes to filling out forms – no matter how bad they are, clinical staff still endeavour to fill them out as best they can, and usually do a pretty amazing job. How successful this is from a data point of view, is a matter for further debate and investigation, I guess. There is no doubt we have to do a better job when we try to represent these forms in electronic format.
We also discussed that this modelling and design process was an opportunity to streamline and refine workflow and records rather than perpetuating outmoded or inappropriate or plain wrong ways of doing things.
So, an outline of the openEHR modelling methodology as we used it:
- Mind map the domain – identify the scope and level of detail required for modelling (in this case, representing just one paper form)
- Identify:
- existing archetypes ready for re-use;
- existing archetypes requiring modification or specialisation; and
- new archetypes needing development
- Specialise existing archetypes – in this case COMPOSITION.encounter to COMPOSITION.encounter-chemo with the addition of the Protocol/Cycle/Day of Cycle to the context
- Modify existing archetypes – in this case we identified a new requirement for a SLOT to contain CTCAE archetypes (identical to the SLOT added to the EVALUATION.problem_diagnosis archetype for the same purpose). Now in a formal operational sense, we should specialise (and thus validly extend) the archetype for our local use, and submit a request to the governing body for our additional requirements to be added to the governed archetype as a backwards compatible revision.
- Build new archetypes – in this case, an OBSERVATION for recording the state of the inserted intravenous access device. Don't take too much notice of the content – we didn't nail this content as correct by any means, but it was enough for use as an exercise to understand how to transfer our collective mind map thoughts directly to the Archetype Editor.
- Build the template.
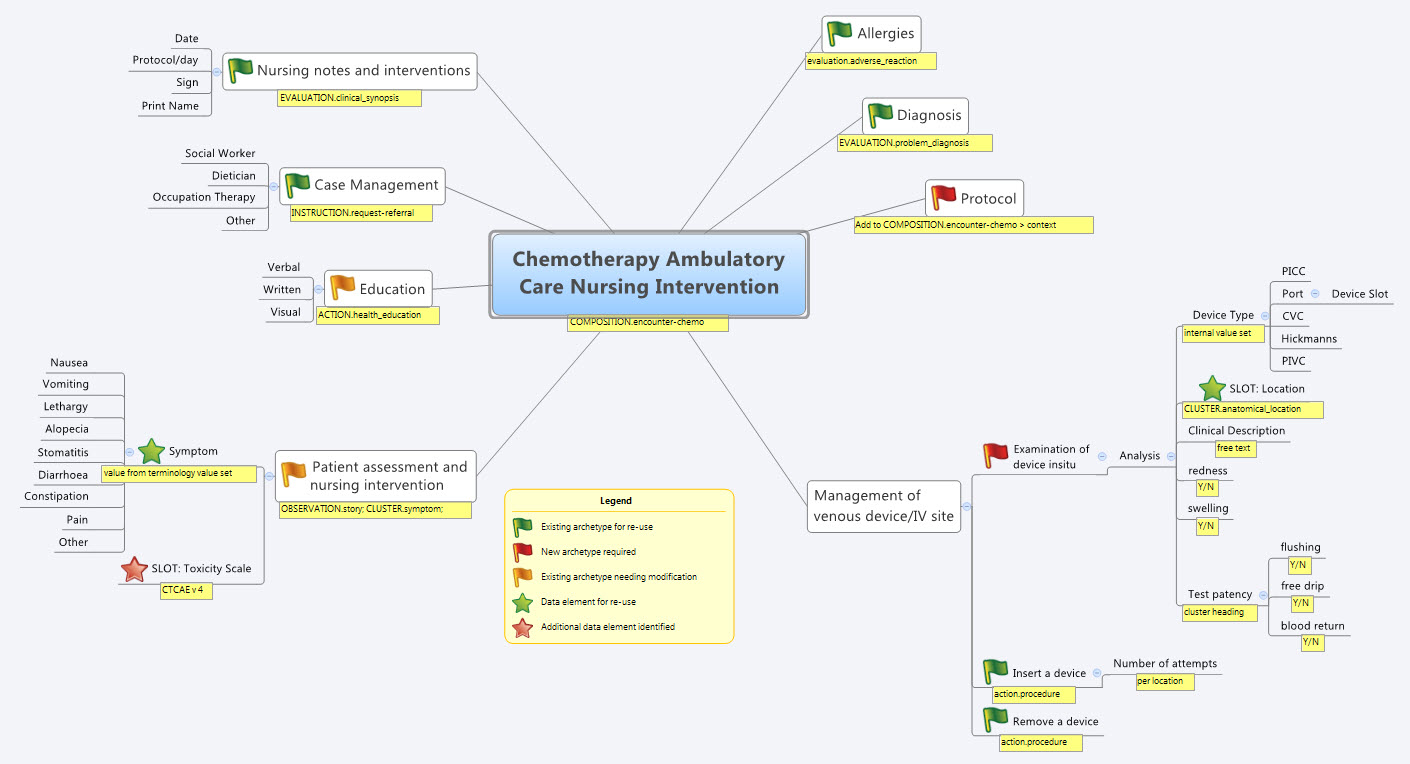
So by the end of the second day, the trainee modellers had worked through a real-life use-case including extended discussions about how to approach and analyse the data, and with their own hands were using the clinical modelling tooling to modify the existing, and create new, archetypes to suit their specific clinical purpose.
What surprised me, even after all this time and experience, was that even in a relatively 'new' domain, we already had the bulk of the archetypes defined and available in the NEHTA CKM. It just underlines the fact that standardised and clinically verified core clinical content can be re-used effectively time and time again in multiple clinical contexts.The only area in our modelling that was missing, in terms of content, was how to represent the nurses assessment of the IV device before administering chemo and that was not oncology specific but will be a universal nursing activity in any specialty or domain.
So what were we able to re-use from the NEHTA CKM?
- COMPOSITION.encounter
- EVALUATION.adverse_reaction – one instance per adverse reaction included in a adverse reaction list
- EVALUATION.clinical_synopsis
- EVALUATION.problem_diagnosis – one instance per diagnosis included in a problem list
- INSTRUCTION.request-referral – one instance per referral requested
- ACTION.health_education
- ACTION.procedure – with two instances for different purposes
…and now that we have a use-case we could consider requesting adding the following from the openEHR CKM to the NEHTA instance:
- OBSERVATION.story
- CLUSTER.symptom – with multiple instances for each symptom identified
And the major benefit from this methodology is that each archetype is freely available for use and re-use from a tightly governed library of models. This openEHR approach has been designed to specifically counter the traditional EHR development of locked-in, proprietary vendor data. An example of this problem is well explained in a timely and recent blog - The Stockholm Syndrome and EMRs! It is well worth a read. Increasingly, although not so obvious in the US, there is an increasing momentum and shift towards approaches that avoid health data lock-in and instead enable health information to be preserved, exchanged, aggregated, integrated and analysed in an open and non-proprietary format - this is liquid data; data that can flow.
The Times, They Are a-Changin’...
Channelling Bob Dylan? Not quite! But it is interesting to see some emerging HL7 and openEHR activity, at least in this little part of the world – Australia and New Zealand :) Maybe this is a model for the rest of the world - at least food for thought!
For too many long years there appears to have been a palpable barrier between the HL7 and openEHR communities. Some individuals have managed to bridge it, but there has definitely been a reluctance to engage at organisational level. It stems from before my time; I suspect vocal personalities with strong, diverging opinions were at the root. To some, it is a little like a religious argument – where "only my way is the right way"!
Be that as it may - the barrier appears to be softening and became evident to me for the first time back in January last year as I attended the HL7 meeting in Sydney. A full day openEHR workshop was presented by a diverse group of Australian companies plus NEHTA experts; Bob Dolin in attendance, amongst others. Keith Boone tweeted his initial impression of the openEHR approach after I demonstrated our tooling and then blogged about it. My thoughts were captured in my Adventures of a clinician in HL7 post.
Fast forward to 2012…
You may have seen some announcements from New Zealand. Firstly, publication in April of the Health Information Exchange Architecture Building Blocks where they specified "2.3.2 The data definitions of the Content Model shall be formulated as openEHR archetypes" within the "10040.2 HIE Content Model, a framework for the creation of a common set of logical data definitions" document.
And secondly: HL7 New Zealand and the openEHR Foundation signed a Statement of Collaboration - also announced April 2012. Now there's a headline that might have been a surprise to many – HL7 NZ & openEHR clearly intending to work closely together!
Only last Thursday Hugh Leslie & I participated in a seminar, "Bringing the Electronic Health Record to Life," organised by HL7 NZ, Health Informatics New Zealand (HINZ) and the University of Auckland. Prof Ed Hammond, 'the father of HL7', keynoted the meeting: "EHR - The Killer App". In the afternoon mini-tutorials, David Hay presented on FHIR, and Hugh, I and Koray Atalag presented a little about our openEHR work, including clinical knowledge governance and clinician engagement. Koray (a HL7 NZ member and openEHR localisation program coordinator) announced within the meeting that HL7 NZ is the likely organisation to auspice a NZ chapter of openEHR. Now that definitely has to start to change the openEHR/HL7 dynamic somewhat, even if HL7 NZ is a relatively small international affiliate :). The HL7 NZ leadership, to their absolute credit, are certainly not being constrained by any traditional 'turf wars'.
The following day, last Friday, Hugh and I presented a full day workshop on openEHR, again sponsored by HL7 NZ, HINZ and the University of Auckland. As I understand it, this was the first opportunity for the openEHR approach to be socialised with the broader healthIT community in NZ; about 25 in attendance including members of the HL7 NZ Board, vendors, and regional and HealthIT Board reps. The focus was on how openEHR could support the creation of a range of technical artefacts to meet NZ's requirements for CDA messaging (and beyond), generated from a cohesive and governed pool of clinical content models.
Interestingly we had a surprise attendee for the workshop – Ed Hammond joined us for the whole day. I won't presume to guess what Ed has taken away from the day, although he did offer up a comment to the group about the value of exploring use of archetype content directly within CDA.
Post workshop one of the attendees tweeted:
"At #HINZ #openEHR talks last 2 days. openEHR is a fantastic foundation for practical action. Left knowing steps I will take. How cools that!"
And of course, there is an HL7 AU meeting in Sydney early next week entitled "FHIR? CIMI? openEHR? What's the Future of eHealth & mHealth Standards?" The agenda:
- Keynote: Ed Hammond (again) – "FHIR, CIMI and openEHR - What's the Future for eHealth Standards?". [It will be very interesting to hear his opinion after last week's openEHR exposure.]
- Grahame Grieve: "FHIR – What is it? Why has it suddenly become so popular?"
- Hugh Leslie: "Recent developments in openEHR and CDA", and
- I'll be reporting on the CIMI project.
It would be an interesting day to be a fly on the wall! 2 HL7-ers and 2 openEHR-ers addressing an HL7 meeting - all exploring alternatives to the current approaches!
So, keep your eye on the space where HL7 intersects with openEHR – might be some interesting developments.
_______________________
Within the openEHR community, and definitely within Ocean Informatics where I work, we are certainly finding that significant interest is being certainly generated from many sources about the process of using standardised and governed openEHR clinical content as a means to generate range of technical artefacts, including CDA. The New Zealand national interest and activity is evident, as outlined above. And in addition:
- In Australia, NEHTA has piloted the use of clinician-reviewed archetypes from the NEHTA Clinical Knowledge Manager as the start point for generating a number of the PCEHR technical specifications. This work is ongoing and being extended.
- CIMI, the initiative that grew out of HL7 but is now independent, is seeking to develop an internationally agreed approach to clinical modelling and generation of multiple technical outputs. It has already agreed to utilise openEHR ADL 1.5 as its modelling formalism and is using the openEHR Reference Model as the starting point for developing a CIMI Reference Model. We watch this progress with interest.
- And Brazil's national program has recently reconfirmed its intention to commence using openEHR.
Whether the final solution is openEHR or CIMI or even something else, I think that the advent of standardised clinical models as the common starting point for generation of a range of technical outputs is upon us. Ignore it at your peril. And specifically, I would suggest that HL7 International should be considering very seriously how to embrace this new approach.
Sticking with the quasi-gospel theme, maybe it is now a bit more like Curtis Mayfield's "People Get Ready":
People get ready There's a train a-coming You don't need no baggage Just a-get on board
Let's leave our baggage behind, get on the 'train' together to collaborate and create something that transcends any health IT domain turf war! Don't get left behind...
The ultimate PHR?
I've been interested in the notion of a Personal Health Record for a long time. I was involved in the development of HotHealth, which launched at the end of 2000, a not-so-auspicious year, given the dot com crash! By the time HotHealth was completed , all the potential competitors identified in the pre-market environmental scan were defunct. It certainly wasn't easy to get any traction for HotHealth take-up and yet only recently it has been retired. For a couple of years it was successfully used at the Royal Children's Hospital, cut down and re-branded as BetterDiabetes to support teenagers self-manage their diabetes and communicate with their clinicians, but it wasn't sustained.
This is not an uncommon story for PHRs. It is somewhat comforting to see that the course of those such HealthVault and GoogleHealth have also not been smooth and fabulously successful :-)
Why is the PHR so hard?
In recent years I participated in the development of the ISO Technical Report 14292:2012: Personal health records -- Definition, scope and context. In this my major contribution seemed to be introducing the idea of a health information continuum.
However in the past year or so, my notion of an ideal PHR has moved on a little further again. It has arisen on the premise of a health record platform in which standardised health information persists independently of any one software application and can be accessed by any compliant applications, whether consumer- or clinician-focused. And the record of health information can be contributed to by any number of compliant systems - whether a clinical system, a PHR or smartphone app. The focus is on the data, the health record itself; not the applications. You will have seen a number of my previous posts, including here & here!
So, in this kind of new health data utopia, imagine if all my weights were automatically uploaded to my Weight app on my smartphone wirelessly each morning. Over time I could graph this and track my BMI etc. Useful stuff, and this can be done now - but only into dead-end silos of data within a given app.
And what if a new fandangled weight management application came along that I liked better - perhaps it provided more support to help me lose weight. And I want to lose weight. So I add the new app to my smartphone and, hey presto, it can immediately access all my previous weights - all because the data structure in both apps is identical. Thus the data can be unambiguously understood and computed upon within the second app without any data manipulation. Pretty cool. No more data silos; no more data loss. Simply delete the first app from the system, and elect to keep the data within my smartphone health record.
And as I add apps that suit my lifestyle, health needs, and fitness goals etc, I'm gradually accumulating important health information that is probably not available anywhere else. And consider that only I actually know what medicines I'm taking, including over the counter and herbals. The notion of a current medication list is really not in the remit of any clinician, but the motivated consumer! And so if I add an app to start to manage my medications or immunisations this data could be also used across in yet another compliant chronic disease support app for my diabetes or asthma or...
I can gradually build up a record of health information that is useful to me to manage my health, and that is also potentially useful to share with my healthcare providers.
Do you see the difference to current PHR systems?
I can choose apps that are 'best of breed' and applicable to my need or interest.
I'm not locked in to any one app, a mega app that contains stuff I don't want and will never use, with all the overheads and lack of flexibility.
I can 'plug & play' apps into my health record, able to change my mind if I find features, a user interface or workflow that I like better.
And yet the data remains ready for future use and potentially for sharing with my healthcare providers, if and when I choose. How cool is that?
Keep in mind that if those data structures were the same as being used by my clinician systems, then there is also potential for me to receive data from my clinicians and incorporate it into my PHR; similarly there is also potential for me to send data to my clinician and give them the choice of incorporating this into their systems - maybe my blood glucose records directly obtained from my glucometer, my weight measurements, etc. Maybe, one day, even MY current medicine list!
In this proposed flexible data environment we are avoiding the 'one size fits all', behemoth approach, which doesn't seem to have worked well in many situations, both clinical systems or personal health records. Best of all the data is preserved in the non-proprietary, shared format - the beginnings of a universal health record or, at least, a health record platform fully supporting data exchange.
What do you think?
Preserving health data integrity
How valuable do we really think health data is? How seriously do we take our responsibility to preserve the integrity of our health data? Probably not nearly as much as we should.
Consider the current situation of most clinicians or organisations when purchasing a clinical EHR system. What do they look for? Many possible answers are obvious, but there is one question that I suspect very few are asking. How many consider what data they will be able to export and convert to another format, preserving the current data integrity, at the end of the typical 5-10 year life span of the application? Am I wrong if I suggest it is not many at all?
Despite all the effort that we clinicians put into entering detailed data to create a quality health record we don't seem to often consider the " What next?" scenario. How much and precisely what data will we be able to safely extract, export, transfer or convert into the next, inevitable, clinical system? Ironically, we are simultaneously well aware that clinical systems have a limited technical life span.
Any and all of the health data in a health record is an incredibly valuable asset to the holder, to the patient (if these are not the same entities) and to those downstream with whom we may share it in the future - in terms of $$ invested; manpower resources used to capture, store, classify, update and maintain it; and not least the future value that comes from appropriate and safe clinical decisions being made upon the integrity of existing EHR data.
Yet we don't seem to consider it much... yet. However, as more clinicians are creating increasing amounts of isolated pockets of health data, we should be thinking about it very hard.
Every time we change systems we put our health data at risk - risk of absolute data loss and risk of possible corruption during the conversion. The integrity of health data cannot be guaranteed each time it is ported into a new system because current methods always require some kind of intervention - mapping, transformations, tweaking, 'cleaning', etc. Small errors can creep in with each data manipulation and which over time, can compromise the safety and value of our health data. On principle we know that the data should not be manipulated, but being limited by our traditional approach to siloed EHR applications, we have previously had little choice.
 We need to change our approach and preserve the integrity of our health data at all costs. After all it is the only reason why we record any facts or activity in an electronic health record - so we can use the data for direct patient care; share & exchange the data; aggregate and analyse the data, and use the data as the basis for clinical decision support.
We need to change our approach and preserve the integrity of our health data at all costs. After all it is the only reason why we record any facts or activity in an electronic health record - so we can use the data for direct patient care; share & exchange the data; aggregate and analyse the data, and use the data as the basis for clinical decision support.
We should not be focused on the application alone.
Apps will come and go, but we want our health data to persist - accurate and safe for clinical use - beyond the life span of any one clinical software application.
I've said this before, but it's worth saying many times over:
It's. all. about. the. data.
One of the key benefits of the openEHR paradigm is that the data specifications (the archetypes) are defined independently of any specific clinical system or application; are based on an open EHR architecture specification; and are publicly available in repositories such as the Clinical Knowledge Manager. It means that any data that is captured according to the archetype specification is directly usable by any and all archetype-compliant systems. Plus the data is no longer hard-wired into a proprietary application so that it is orders of magnitude easier to accurately share or transfer health data than it has before.
Clinical system vendors that don't directly embrace the archetype-technology may still 'archetype-aware', and can choose to use the archetype specifications as a means to understand the meaning of existing archetyped data and integrate it appropriately into their systems. Similarly they can map from their non-openEHR systems to the archetype specifications as a standardised method for data export and exchange.
The openEHR paradigm enables potential for archetype-compliant systems to share the same archetyped data repository - along the lines of an Apple platform 'plug & play' approach, with applications being added, removed or updated to suit the needs of the end-users, while the data persists intact. No more data conversions needed.
Adapted from Martin van der Meer, 2009
Now that's good news for our health data.
Modelling pregnancy
Step 2: Map clinical concepts to archetypes
Map them to existing archetypes or determine which new ones we need. Determine the state of the existing archetypes – do we need to modify or enhance with additional requirements? Consider all possible use cases for each archetype – the end result will be better if we can be as inclusive as possible for all clinical scenarios.
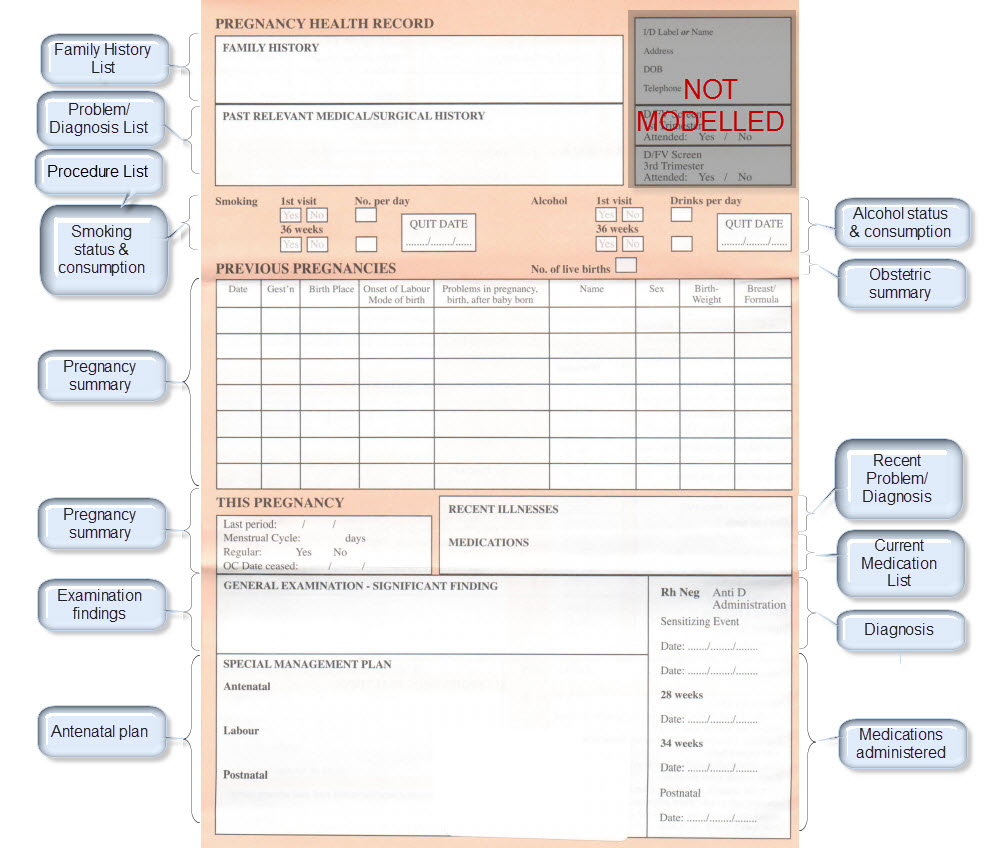
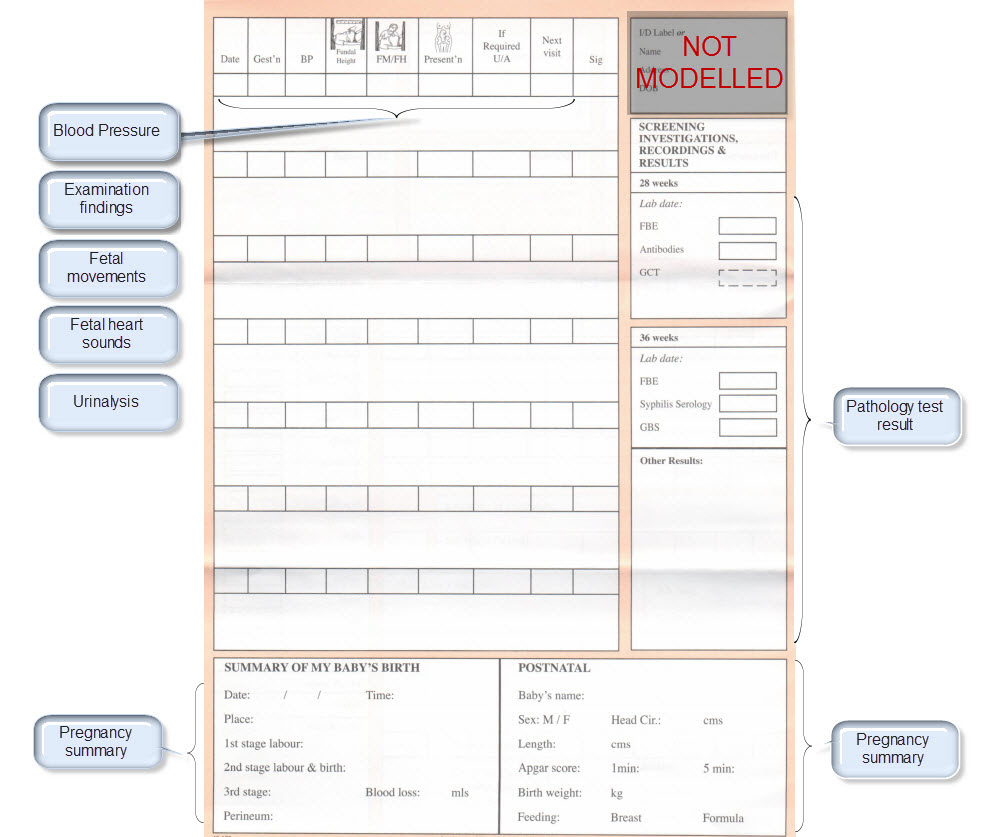
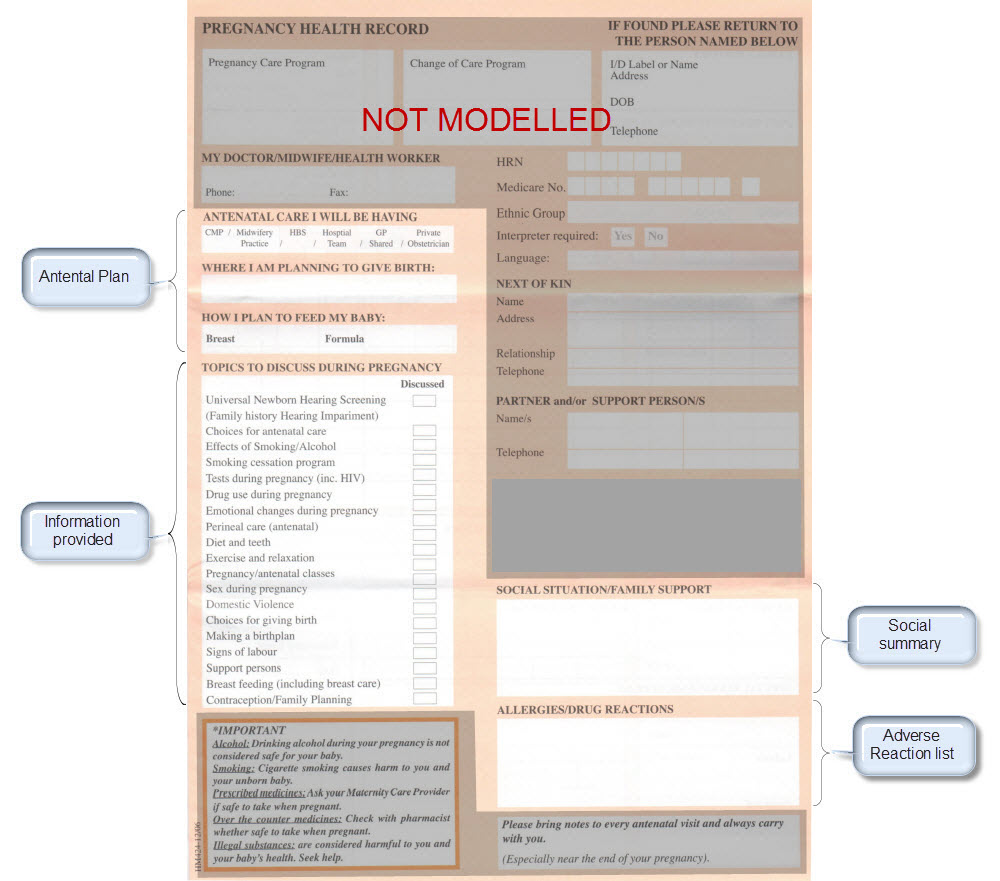
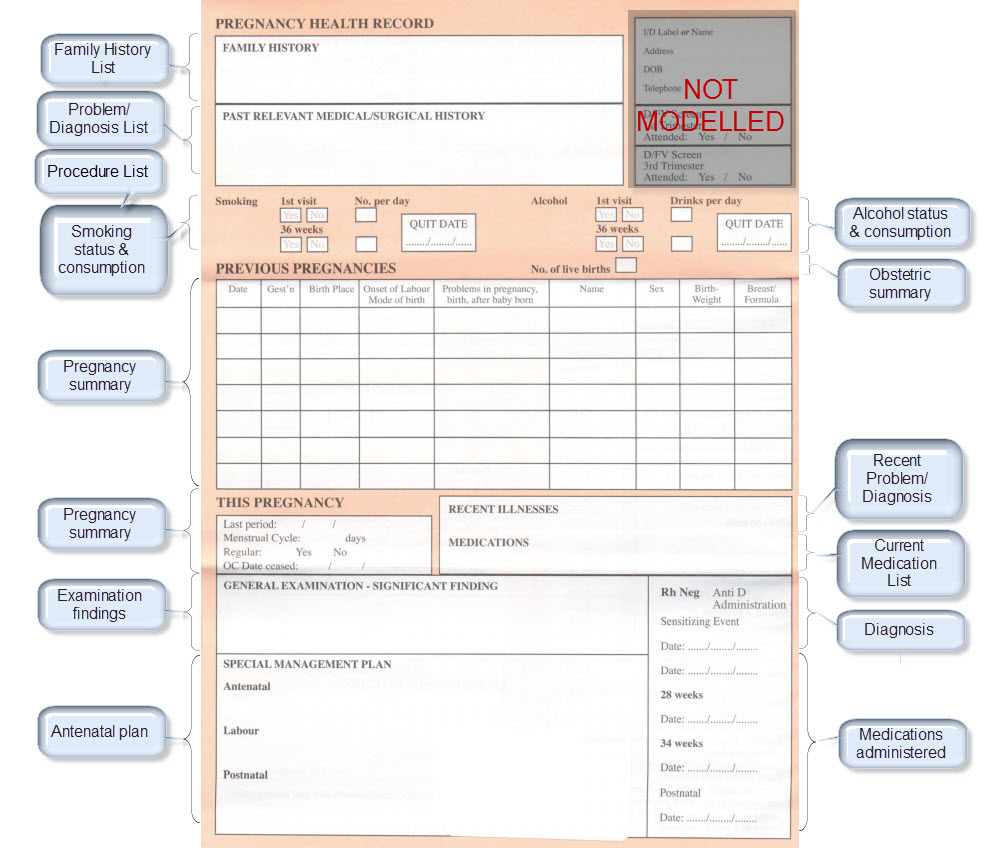
The archetypes identified for this Pregnancy record are:
| Clinical Concept | Comment |
Corresponding archetype concept name NOTE: is linked to the actual archetype in a CKM instance |
| Antenatal Plan | An overarching plan for the patient's antenatal care | Antenatal Plan <INSTRUCTION.antenatal_plan> |
| Information Provided | Details of each piece of health education information discussed or provided to patient | Information Provided <ACTION.health_education> |
| Social Summary | Social Summary <EVALUATION.social_summary> | |
| Adverse Reaction List | Adverse Reaction list is made up of multiple Adverse Reaction entries | Adverse Reaction <EVALUATION.adverse_reaction> |
| Family History List | Family History list is made up of multiple Family History entries | Family History <EVALUATION.family_history> |
| Diagnosis | Problem lists, whether current or past are made up of multiple Problem/Diagnosis entries – the same data pattern will be used in all instances | Problem/Diagnosis <EVALUATION.problem_diagnosis> |
| Problem/Diagnosis List | ||
| Recent Problem/Diagnosis List | ||
| Procedure list | Procedure list is made up of multiple Procedure entries | Procedure <ACTION.procedure> |
| Smoking consumption | Tobacco use <OBSERVATION.substance_use-tobacco> | |
| Alcohol consumption | Alcohol consumption <OBSERVATION.substance_use-alcohol> | |
| Obstetric Summary | Obstetric summary <EVALUATION.obstetric_summary> | |
| Pregnancy Summary | An evolving summary of key data about a single pregnancy – either current or past | Pregnancy summary <EVALUATION.pregnancy_summary> |
| Examination Findings | Examination Findings <OBSERVATION.exam> Examination of the uterus <CLUSTER.exam-uterus> Examination of the fetus <CLUSTER.exam-fetus> | |
| Current Medication List | Medication list is made up of multiple Medication instruction entries | Medication instruction <INSTRUCTION.medication> |
| Medication administered | Medication action <ACTION.medication> | |
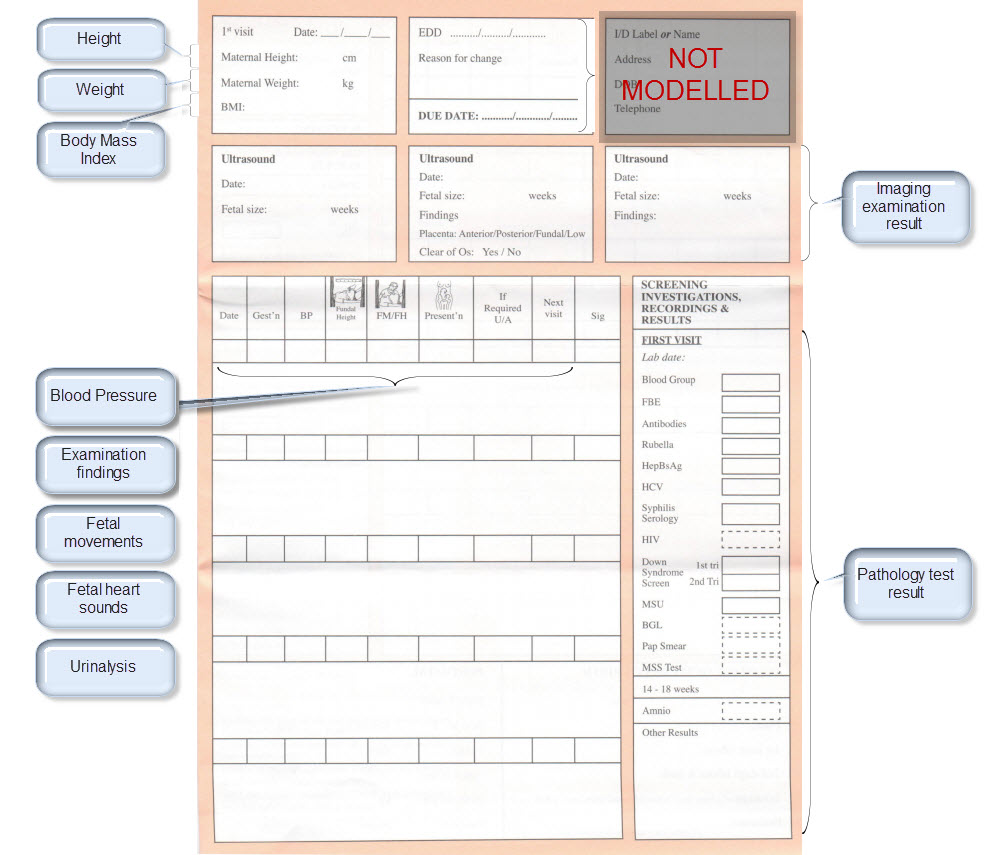
| Height | Height/Length <OBSERVATION.height> | |
| Weight | Body weight <OBSERVATION.body_weight> | |
| Body Mass Index | Body Mass Index <OBSERVATION.body_mass_index> | |
| Blood Pressure | Blood Pressure <OBSERVATION.blood_pressure> | |
| Fetal Movements | Fetal Movements <OBSERVATION.fetal_movements> | |
| Fetal heart sounds | Heart rate and rhythm <OBSERVATION.heart_rate> | |
| Urinalysis | The pattern for urinalysis is identical to the pathology test results, and in some cases will be performed in the lab, so the same pattern will be used | Pathology test result <OBSERVATION.pathology_test> |
| Pathology Test results | ||
| Ultrasound results | Imaging examination result <OBSERVATION.imaging_exam> |
KEY: Pink archetype names indicate those that are early drafts. Green archetype names indicate those that are reasonably mature – through previous reviews within CKM Red archetype names indicate those yet to be developed.
Step 3: CKM Review
Within CKM each archetype will undergo review rounds by a range of clinicians, terminologists, software engineers, informaticians and other interested experts. The purpose of each review round will be to fine-tune each archetype so that it meets the requirements for each stakeholder group.
CKM Videos:
Step 4: Create an openEHR template
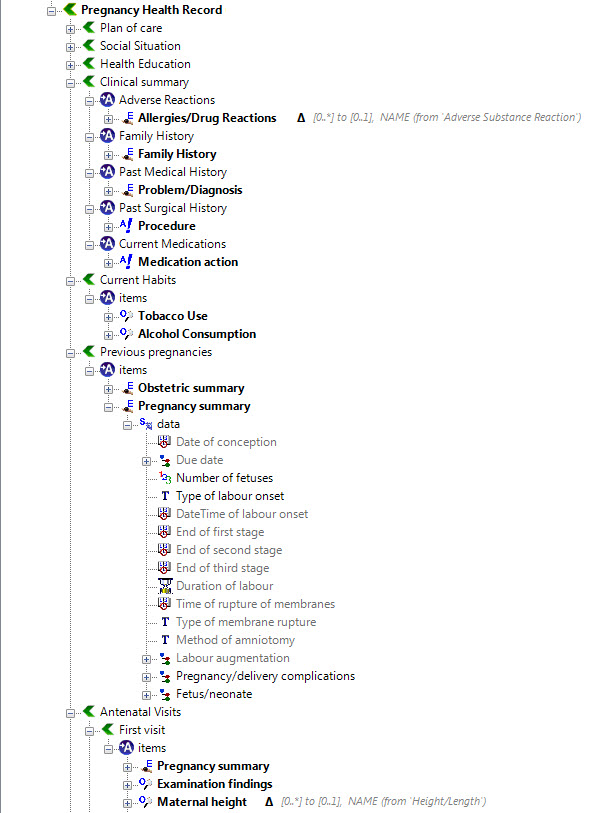
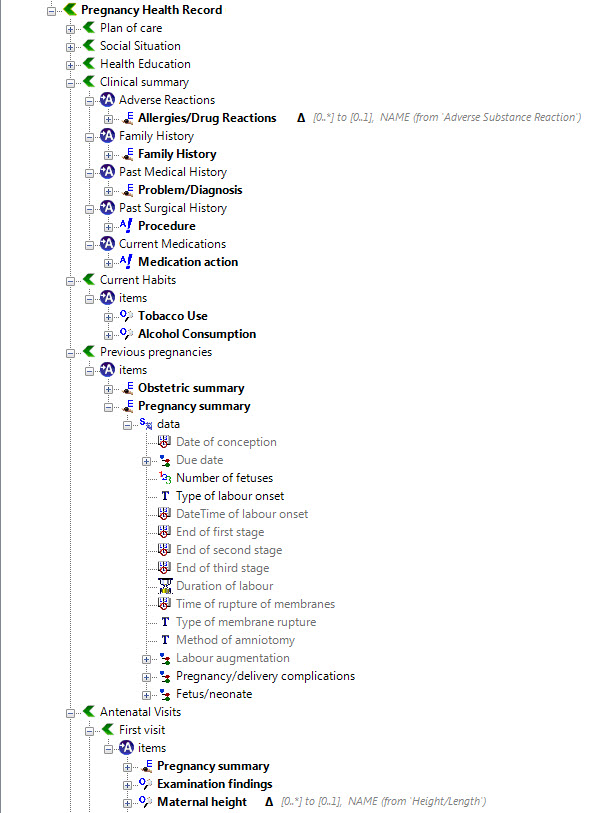
Once community consensus is reached within CKM, the archetypes will be aggregated and constrained in a template to accurately meet the specific use-case requirements for this particular Pregnancy Health Record. Each bold, black heading in the the following screenshot represents an archetype. The Pregnancy Summary archetype has been opened up to see the details. Black text indicates data elements that will be utilised in this use case; grey text indicates inactive data elements.
Other groups may use the same archetypes aggregated in a different order and constrained in a different way to represent their version of the Pregnancy Health Record. As the data in both Pregnancy Records is being recorded according to the same pattern, dictated by the underlying archetype, the information can be exchanged without ambiguity or loss of meaning.
Engaging Clinicians in Clinical Content (in Sarajevo)
Just browsing and found the link to our presentation for a paper the CKM team gave at the Medical Informatics Europe conference in Bosnia, 2009. Thought I'd share it here, in memory of an amazing conference and location:
MIE09: Engaging Clinicians in Clinical Content [PDF]
Our presentation:
[slideshare id=1958920&doc=engagingcliniciansinclinicalcontent-090906091020-phpapp02]
And the reference to Herding Cats is explained (a little) in the embedded video - actually an advertisement for EDS:
[youtube http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Pk7yqlTMvp8&w=425&h=349]
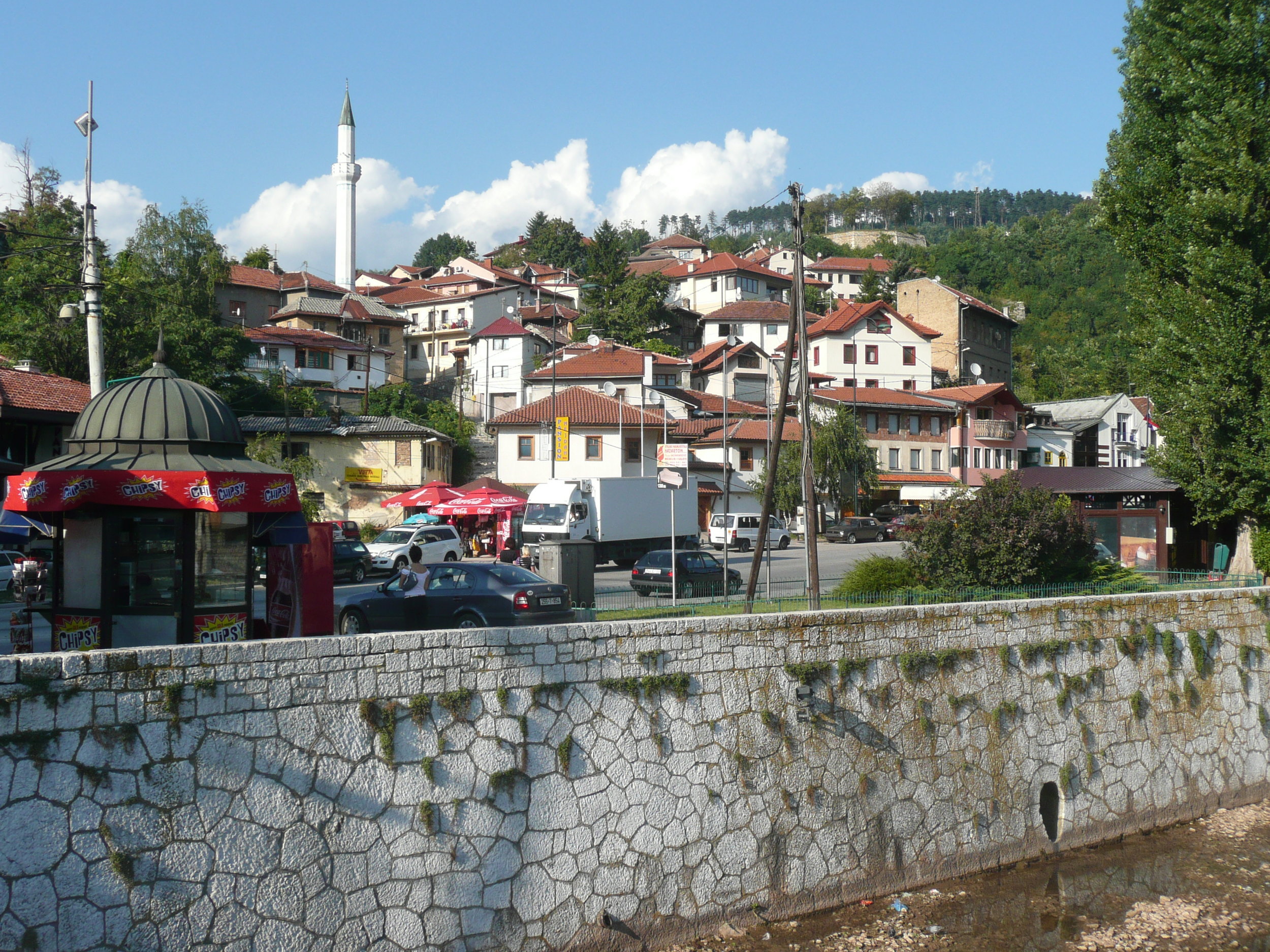
I arrived after a 37 hour flight - Melbourne - London - Vienna - Sarajevo to join my Ocean CKM team - Ian McNicoll and Sebastian Garde. We presented our paper and also ran an openEHR workshop.
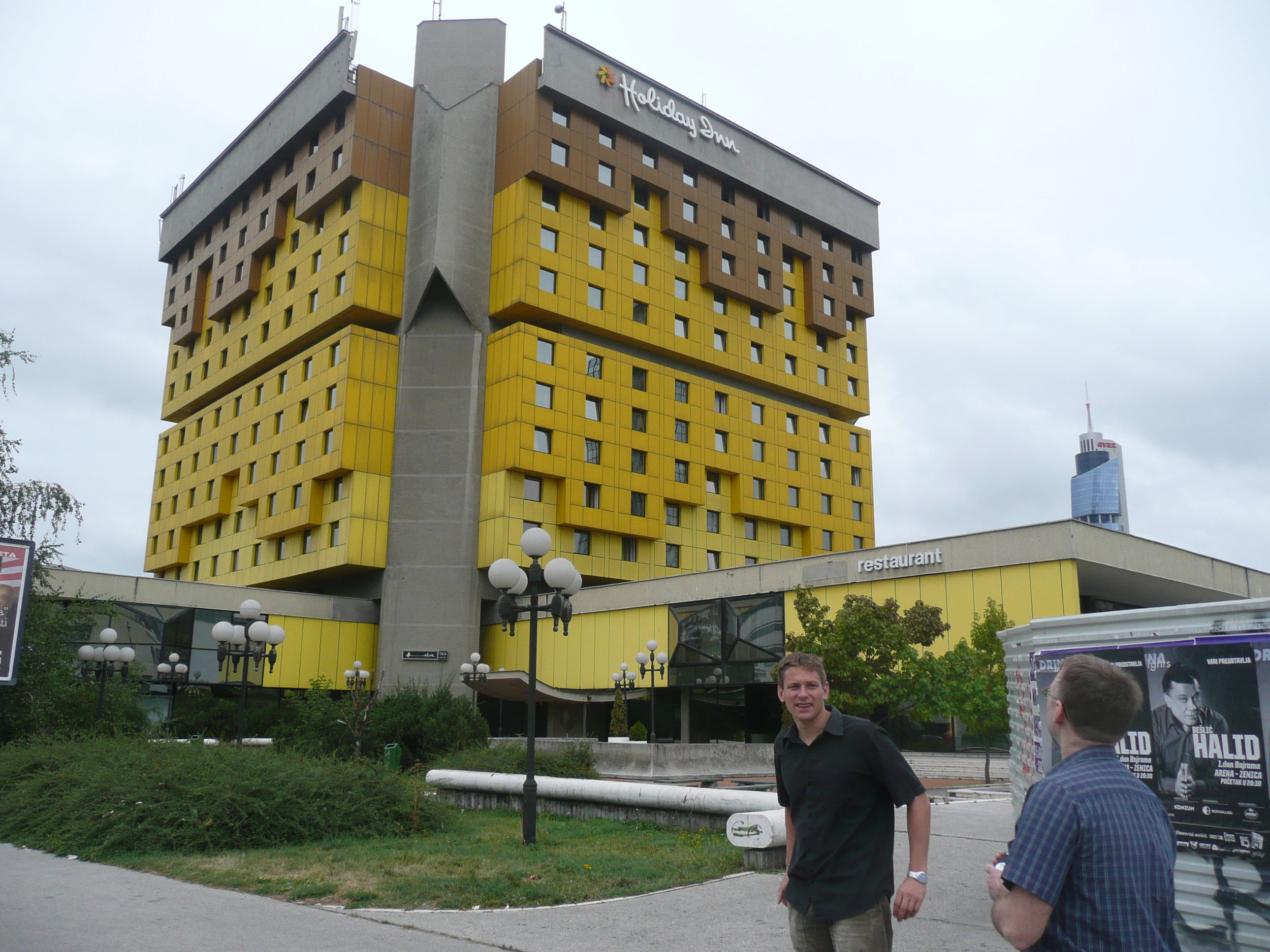
The conference was held at the Holiday Inn in Sarajevo - the hotel in which all the international journalists were holed up during the war, on 'Sniper Alley'.
Despite it being 14 years after the war had ended, raw emotions were palpable many times during the conference. That a pan-European conference was being held in his beloved Sarajevo under his auspice was a very overwhelming event for the Professor of Informatics and he was often seen in tears!
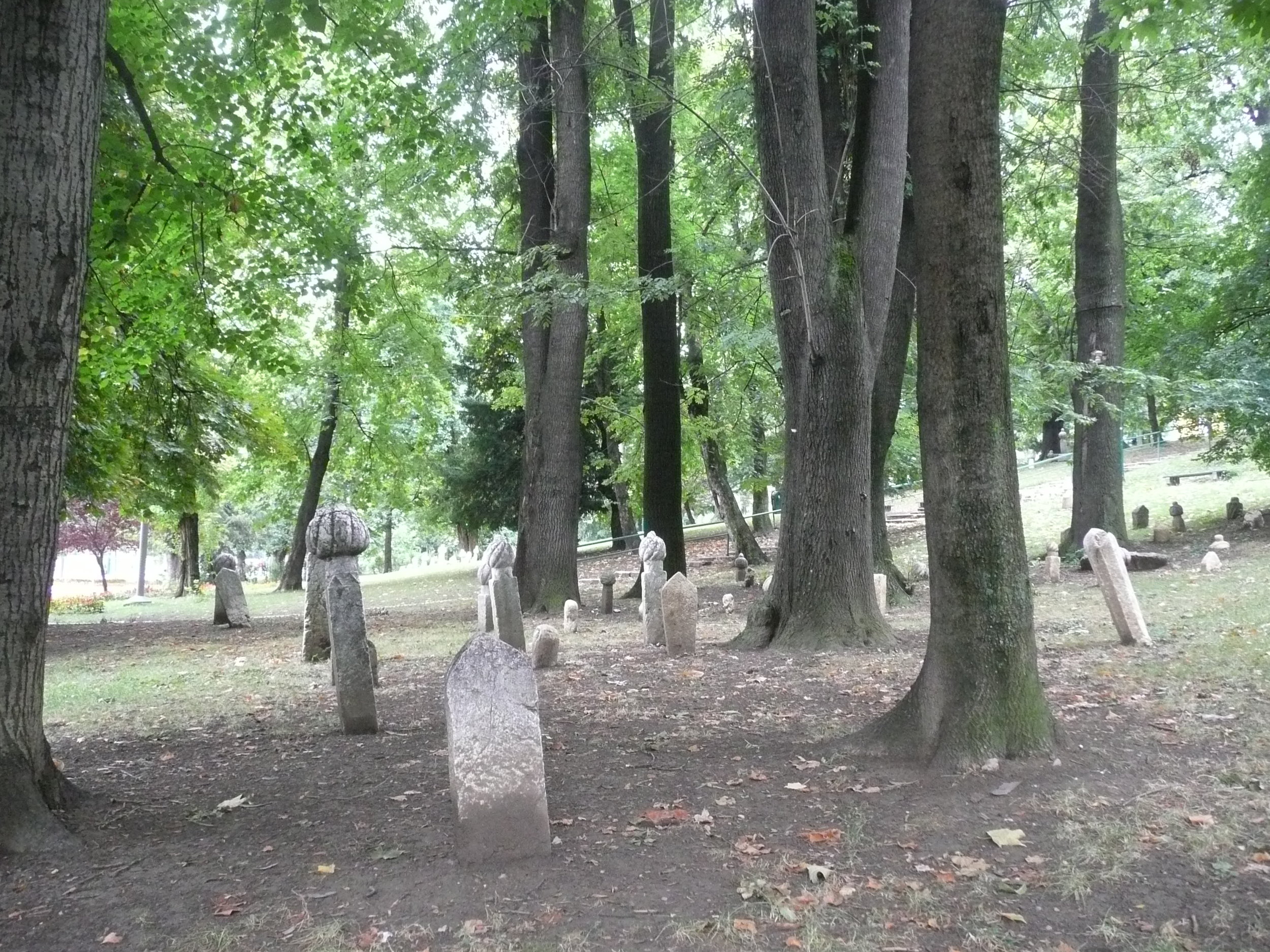
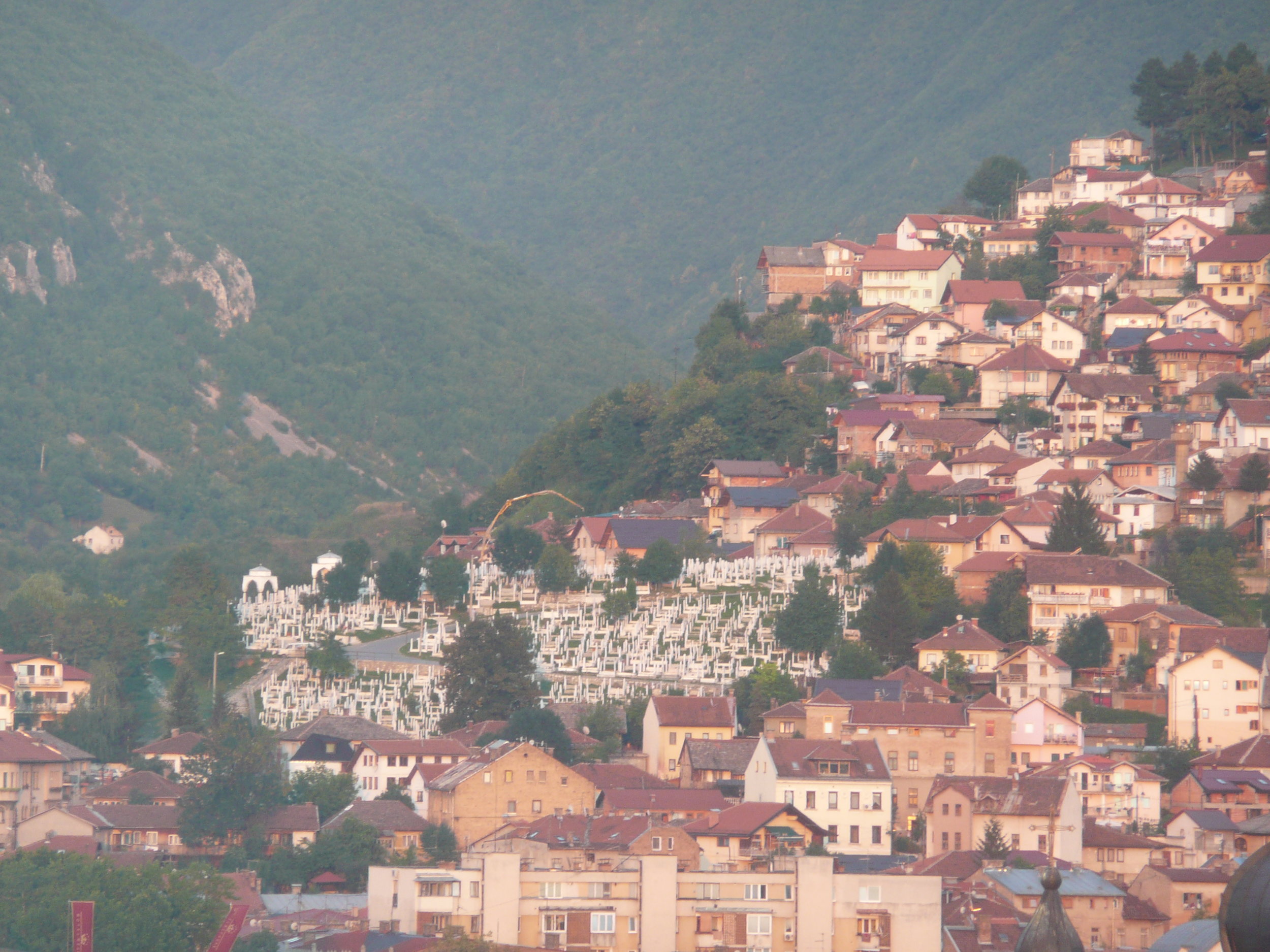
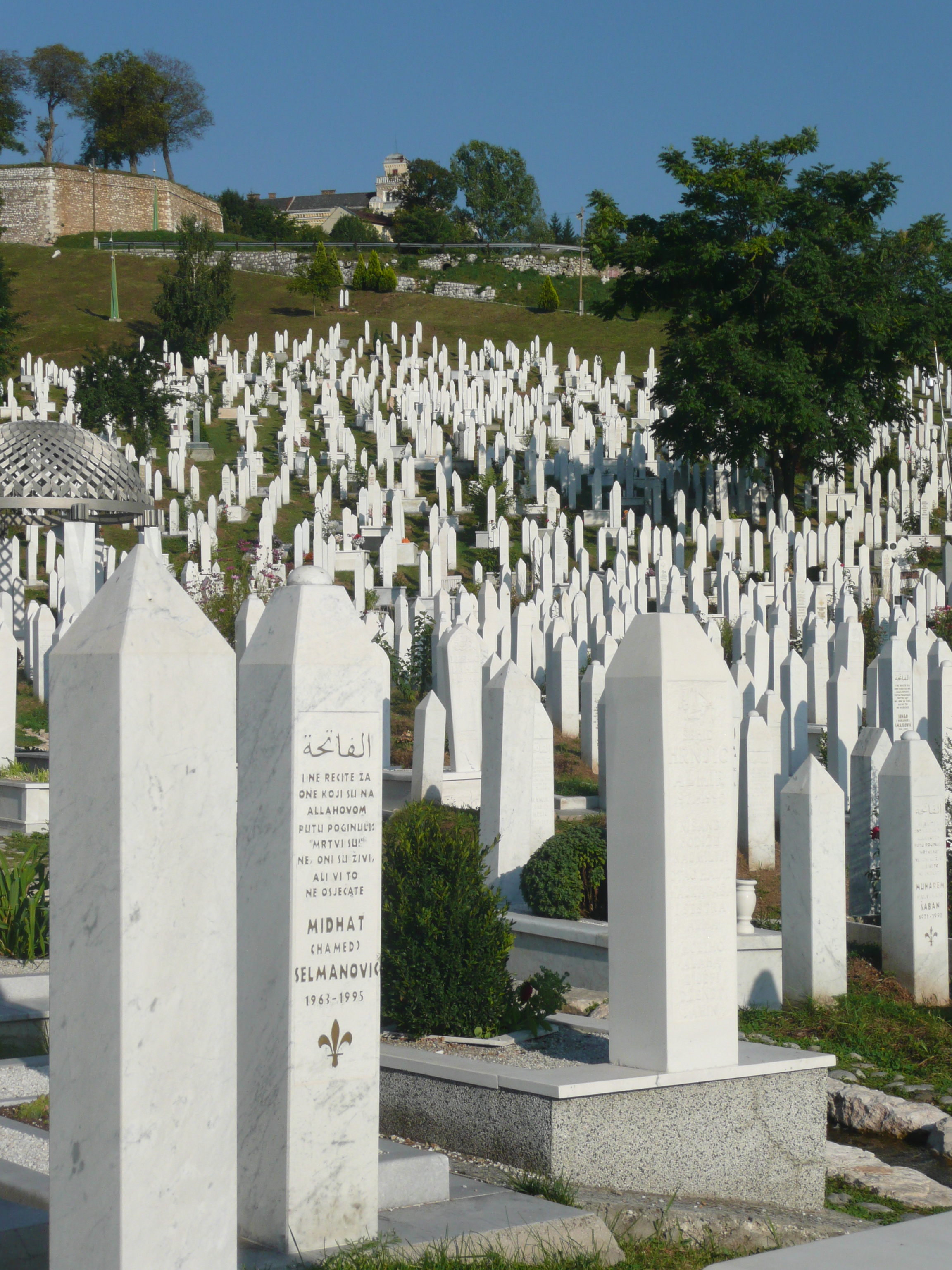
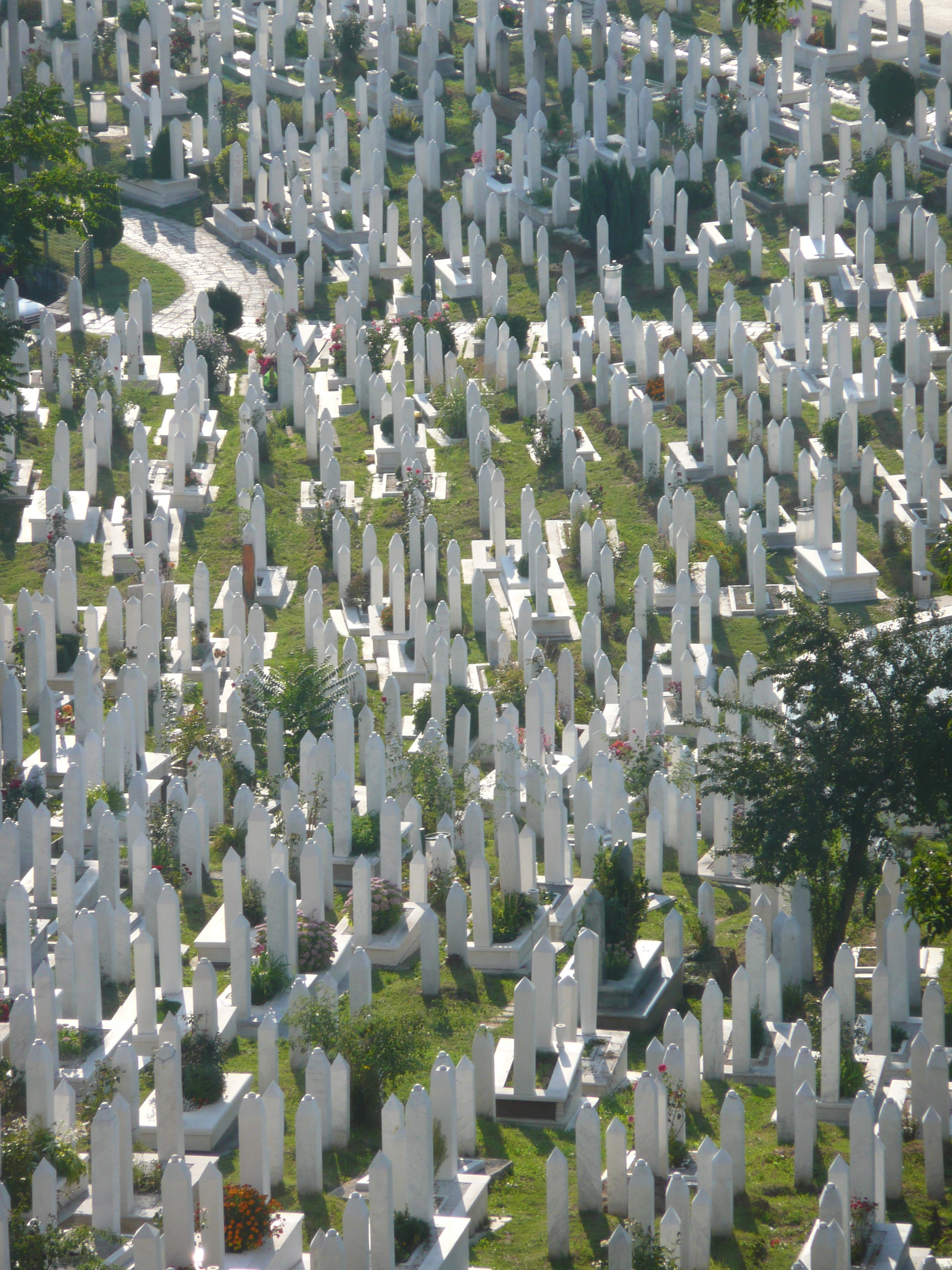
From my hotel room window in the centre of the city I could see 6 cemeteries.
Walking through the inner city we came across many cemeteries, thousands of marble gravestones with the majority representing the young men aged between 18 & 26.
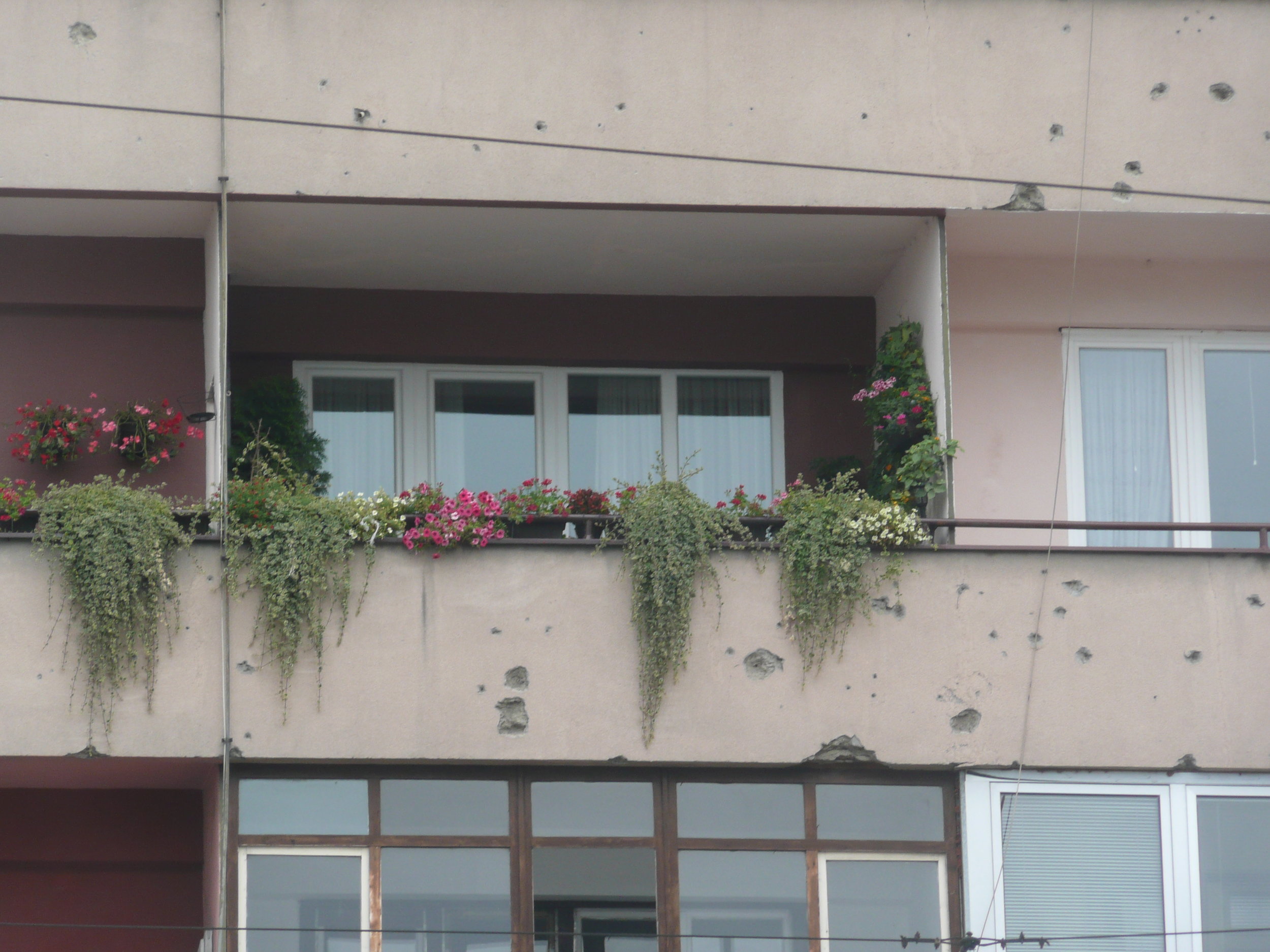
Bullet holes were still very obvious on the walls of buildings.
Yet the city was vibrant, alive and welcoming.
I won't ever forget this visit.
Some photos of the experience: